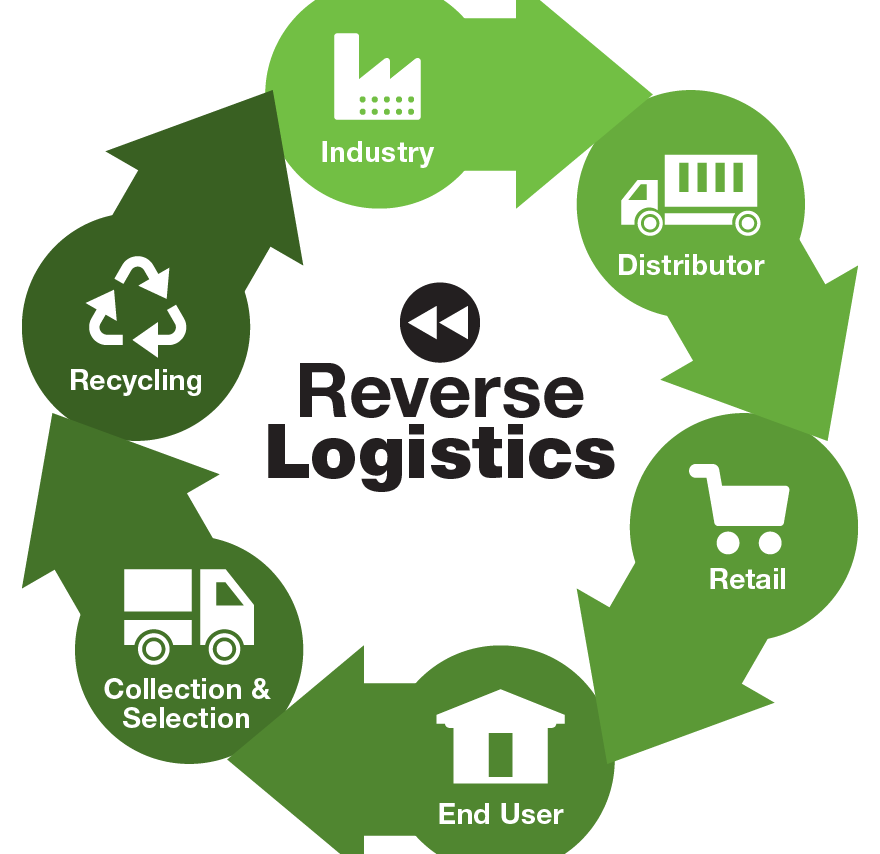
Importance of Reverse Logistic
Reverse logistics is crucial for recovering value from returned goods, reducing waste, and improving sustainability. It enhances customer satisfaction.
In Pakistan’s business landscape, reverse logistics—the process of transporting goods from their final destination back to the manufacturer or distributor for returns, refurbishing, recycling, or disposal—has become increasingly important. Effectively handling product returns has become essential for preserving customer satisfaction and cutting expenses as the retail and e-commerce sectors expand. Effective returns management helps companies in a number of important ways:
Reverse logistics
The process of moving goods from the customer back to the manufacturer or seller, including returns, recycling, and disposal. It involves the flow of products in the opposite direction of traditional supply chains.
Returns management
The administration and handling of returned products, ensuring they are processed efficiently. This includes return authorization, product inspection, restocking, and sometimes refurbishment or disposal.
Supply chain optimization
Improving the efficiency of supply chain processes, including reverse logistics, to minimize costs, reduce time, and improve customer service. In reverse logistics, this often involves streamlining the returns process.
Customer satisfaction
The level of contentment customers feel when dealing with a business, especially regarding returns and exchanges. Efficient reverse logistics systems enhance customer satisfaction by providing a smooth returns experience.
Sustainability
Incorporating environmentally friendly practices into logistics and returns management, such as reducing waste, recycling returned goods, or repurposing products. Sustainability in reverse logistics can lead to a more responsible business model.
Cost reduction
One of the primary goals of reverse logistics is reducing costs associated with product returns, refurbishments, and disposal. By optimizing the reverse supply chain, businesses can minimize losses from returned goods.
Inventory management
The process of overseeing and controlling the storage, availability, and movement of products, including those returned through reverse logistics. Proper inventory management helps in reducing overstock and improving restocking efficiency.
Waste reduction
Reverse logistics can play a key role in minimizing waste by enabling recycling, refurbishing, or reselling of returned products instead of disposing of them. This also ties into sustainability efforts.
Circular economy
An economic model where resources are reused and recycled as much as possible. In reverse logistics, this concept applies through product recovery, recycling, and the use of returned goods in the production of new products.
Product recovery
The process of retrieving returned products for the purpose of repair, refurbishment, or recycling. It is a critical part of reverse logistics and can provide value by turning returns into usable goods.
Competitive advantage
Businesses that implement efficient reverse logistics systems gain a competitive edge by reducing costs, improving customer experience, and promoting sustainability. This can differentiate them in the market and attract more customers.